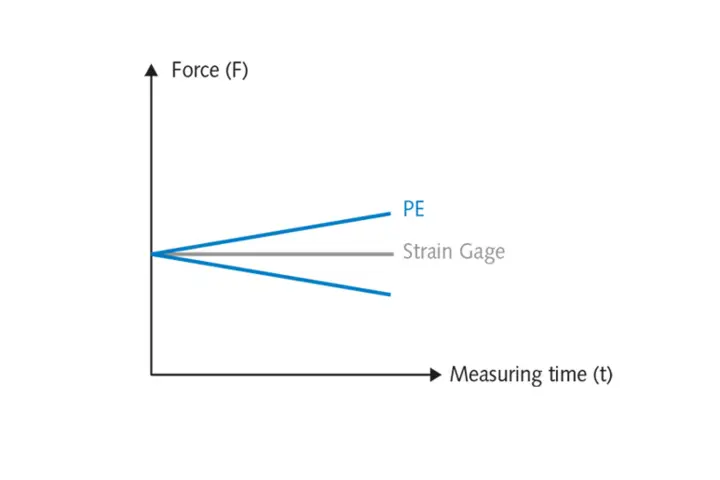
Piezoelectric principle: Capturing electrical charge
The force is applied to a piezoelectric crystal and causes a charge shift at the molecular level and within the lattice structure. This electric charge is captured at the crystal surface and converted into a voltage signal by means of a so-called charge amplifier.
Advantage:
The deformation is extremely small since the charge effect is caused by shifts within the atomic structure. This enables the realization of extremely rigid structures featuring high natural frequencies. This is ideal for capturing very fast or high-frequency measurement events.
Disadvantage:
The electric charge is very volatile. Where there is no perfect isolation, charge is lost over time. This makes long-term stable measurements difficult, especially if you want to measure small forces. Furthermore, a piezoelectric sensor is far more subjected to temperature changes.
The strain gauge principle: Capturing a change in electric resistance induced by elastic deformation
The force is applied to a spring body, which deforms proportionally to the force exerted. This deformation again causes compression or stretching of the attached strain gauges and thus a change in their electrical resistance. By using a simple electrical measuring bridge circuit, a usable voltage signal can be generated.
Advantage:
Measurements are very long-term stable and changes in temperature can be better compensated. Sensors featuring very high accuracy can be realized.
Disadvantage:
The quality of signal acquisition improves with the grade of the strain gauges’ elastic deformation. That means that its structure is rather soft, featuring a low natural frequency, which is inappropriate for faster-measuring events. Due to deformation, material fatigue and overstrain are additional critical aspects of this measurement principle.