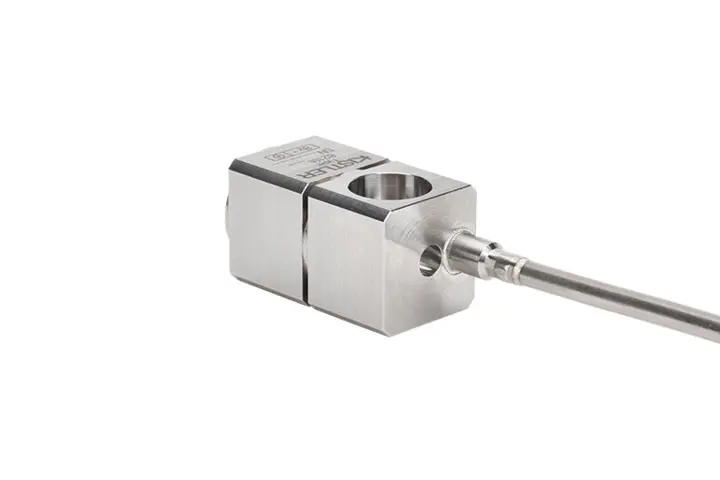
What are high-temperature accelerometers used for?
High-temperature accelerometers are applied for acceleration measurement in harsh environments, for example in space applications (i.e. rocket testing) or monitoring of gas turbines and detonation engines. They are also employed for nuclear power plants.
How is the measuring chain for high-temperature accelerometers built up?
Apart from the sensors themselves, differential charge amplifiers and low-noise hardline and softline cables ensure that a high measurement quality is achieved. Additionally, Ex-certified components are used for application in harsh environments.
What types of high-temperature accelerometers do exist?
As for accelerometers in general, there is a difference between uniaxial and triaxial sensors: Uniaxial ones only measure in one direction, while triaxial ones capture signals in all three spatial dimensions. Furthermore, there are variants for different temperature limits, i.e. < 260°C, < 480°C and > 700°C as well as certified (ATEX, IECEx) versions for hazardous areas. For research and development purposes, small and lightweight versions are available. Last but not least, market standards for high-temperature accelerometers include square and triangular ARINC footprints.