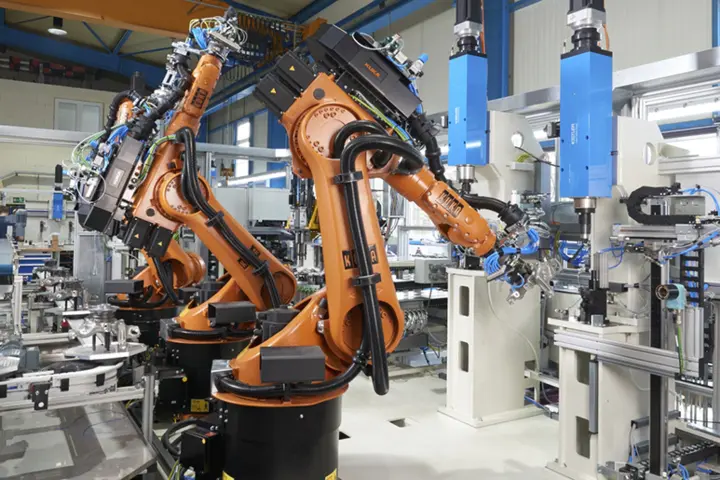
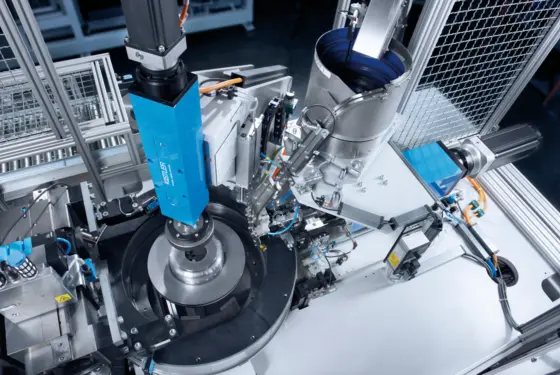
A joining system such as a servo press typically comprises a joining module (also known as a 'joining spindle'), a servo amplifier, and a force-displacement evaluation unit. Process monitoring systems are used for quality assurance. On the basis of data from force and displacement sensors, they evaluate and document the force-displacement profiles (XY curves) for joining and press-fit processes.
As well as monitoring the process, it is also possible to control it in real-time. Various standard functions are available for these purposes, including force cutoff and control, gradient and inflection point detection, as well as a signal or position-based joining.
What advantages do servo presses or electromechanical joining systems offer as compared to hydraulic or pneumohydraulic joining systems?
To an increasing extent, servo presses or electromechanical joining systems are replacing conventional hydraulic or pneumohydraulic systems. The main factors that influence the choice of this technology are a better energy balance, precise control and flexibility, and a lower TCO (total cost of ownership).
Servo presses and/or electromechanical joining systems:
- Play a valuable part in protecting the climate thanks to their better energy balance, yielding the potential for cutting CO2 emissions by up to 90% as compared to other technologies*
- Improve and guarantee product quality thanks to process monitoring during the manufacturing process
- Boost plant productivity thanks to reduced scrap, so operating costs are cut
Where are servo presses / electromechanical joining systems in use?
- Automotive sector and supplier industry
- Medical device industry
- Electronics industry
- Domestic appliances industry
- Power tools
* Study by the University of Kassel (2012)